Power
Power is the rate at which work is done. It is the work/time ratio. The standard metric unit of power is the Watt. As is implied by the equation for power, a unit of power is equivalent to a unit of work divided by a unit of time. Thus, a Watt is equivalent to a Joule/second.
dBm (sometimes dBmW) is an abbreviation for the power ratio in decibels (dB) of the measured power referenced to one milliwatt (mW). It is used in radio, microwave and fiber optic networks as a convenient measure of absolute power because of its capability to express both very large and very small values in a short form. Compare dBW, which is referenced to one watt (1000 mW).
Since it is referenced to the watt, it is an absolute unit, used when measuring absolute power. By comparison, the decibel (dB) is a dimensionless unit, used for quantifying the ratio between two values, such as signal-to-noise ratio.
If one mW as the standard power value, the dB value of a certain power P is defined as:
- P(dBm) = 10log (P(mW)/1mW)
If we base our P in dB in terms of 1 W, so the dB value of this power is defined as:
- P(dBw) = 10 log (P(W)/1W)
Using logarithmic we can convert dBw to dBm using this equation:
- P(dBm) = P(dBW) +30
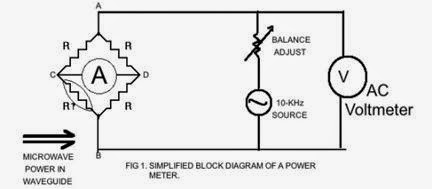
Thermocouples, diode detectors, and thermistors are commonly used as power measurement technology techniques. A thermistor is a type of resistor whose resistance varies significantly with temperature, more so than in standard resistors.
The thermister is represented by RT, is connected in one branch of a wheatstone bridge and inserted into the waveguide. It said to be that the wheatstone bridge is balanced if RT is equal to the R having no current passes through the ammeter. Then the power Po dissipated can be calculated using voltage across the bridge (bet. A and B) and the known value R of the resistors. The Power can now be computed using P=VI. Where Power is the product of voltage and current. Here, in the experiment, will be using a power meter designed to automatically balance the bridge by means of a feedback loop. Power can also be calculated by the difference of the dissipated power and absorbed power.
- Express a power of 2W in dBm.
- Convert a power of -15dBw in watts.
Pw = 0.0316 watts
Notes:
Notes:
In the power meter, why must the audio power be reduced in proportion to the microwave power applied to the thermistor?
- The audio power must be reduced in order to attain ‘equilibrium state’ which is caused by the added microwave, which produces more heating in the thermometer, thus changes its resistance.
Why is it important to match the thermistor to the waveguide when performing a power measurement?
- The thermistor needed to match the waveguide in performing power measurements in order to obtain a precise power reading, and all the incident microwave power will be absorbed by the thermistor.
CONCLUSION:
There are several ways or techniques used in this experiment to get the power at the thermistor mount. In order to get the Power dissipated, the two audio signals must be adjusted to equal the resistances across the thermistor resulting an equilibrium state. In order to have a precise reading in power measurements, thermistor is needed to match the waveguide. Power can also be converted from watts to decibels.

0 comments